In today’s fast-paced academic world, the ability to find relevant and credible research articles is a crucial skill for students, researchers, and professionals alike. Whether you’re writing a literature review, preparing a thesis, or staying current in your field, knowing how to efficiently locate and evaluate scholarly sources is essential.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of finding research articles, from defining your topic to staying updated with the latest publications.
We’ll explore various strategies and tools, including:
- Utilizing academic search engines and databases
- Leveraging institutional resources
- Exploring specialized research networks
- Evaluating source credibility
- Using reference management tools
- Setting up alerts for new research
Table of Contents
Let’s dive into the world of academic research and discover how to find the articles that will drive your scholarly pursuits forward.
Understanding Your Research Topic
Before diving into the search for research articles, it’s crucial to have a clear grasp of your research topic. This initial step sets the foundation for a successful and efficient search process.
The journey to finding relevant research articles begins with a well-defined research question. This question serves as your compass, guiding your search and helping you identify the most pertinent information.
To formulate an effective research question:
- Begin with a general area of interest within your field of study.
- Pinpoint the main ideas or themes you want to explore.
- Ask “how,” “what,” or “why”. Frame your question to encourage investigation rather than simple yes or no answers.
- Ensure your question can be answered within the scope of your research project.
For example, if you’re interested in climate change, a broad question might be “How does climate change affect marine ecosystems?” This question highlights the key concepts (climate change, marine ecosystems) and invites exploration.
Narrowing Down Your Topic for Specificity
Once you have a general research question, it’s time to narrow it down for greater specificity. This step is crucial for several reasons:
- A more specific topic is easier to research and write about comprehensively.
- Narrower topics often lead to more original research angles.
- Specificity allows for a deeper exploration of your chosen subject.
To narrow down your topic:
- Choose one element of your broader question to investigate.
- Restrict your research to a specific region or time.
- Concentrate on a particular group or example within your broader topic.
Using our climate change example, we could narrow it down to: “How has ocean acidification affected coral reef ecosystems in the Great Barrier Reef over the past decade?” This refined question specifies the aspect of climate change (ocean acidification), the ecosystem (coral reefs), the location (Great Barrier Reef), and the time frame (past decade).
Utilizing Academic Search Engines
Once you’ve defined your research topic, the next step is to leverage academic search engines to find relevant research articles. These specialized tools are designed to help you navigate the vast sea of scholarly literature efficiently.
Popular Academic Search Engines
Several academic search engines are widely used by researchers, each with its own strengths:
- Google Scholar: A comprehensive search engine that covers a wide range of academic disciplines. It’s user-friendly and provides access to many free full-text articles.
- PubMed: Primarily focused on life sciences and biomedical research. It’s an excellent resource for healthcare-related topics.
- Web of Science: Offers a robust collection of peer-reviewed journals across multiple disciplines. It’s particularly useful for tracking citations and identifying influential papers.
- JSTOR: A digital library containing a vast collection of academic journals, books, and primary sources. It’s especially valuable for humanities and social sciences research.
- ScienceDirect: Provides access to a large database of scientific and medical research. It’s operated by Elsevier and covers a wide range of scientific disciplines.
Tips for Effective Search Queries
To make the most of these search engines, it’s important to construct effective search queries. Here are some strategies to enhance your search:
Using Keywords and Phrases
- List the most important words or phrases related to your research question.
- Include alternative terms for your key concepts to broaden your search.
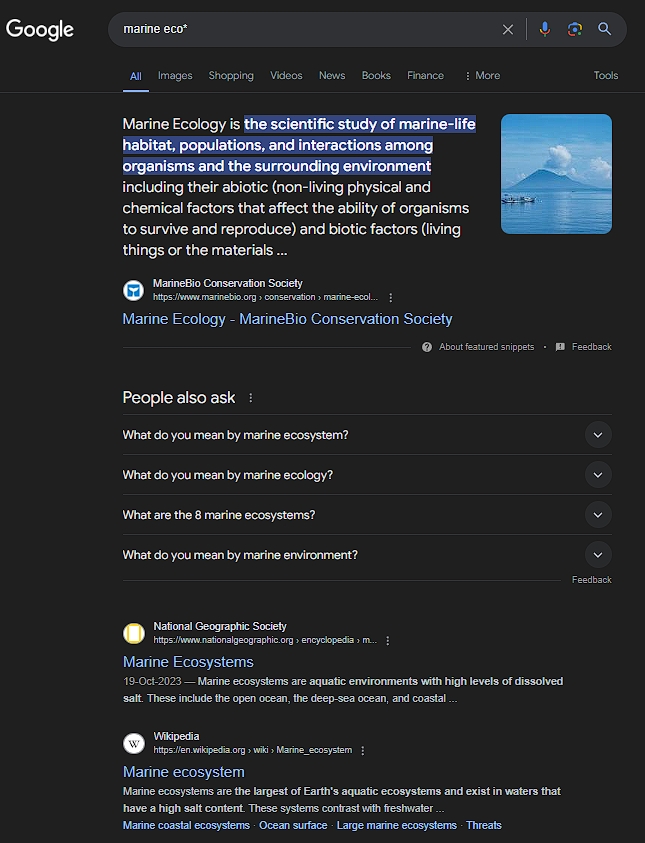
- Use quotation marks to search for exact phrases. For example, “ocean acidification” will yield more precise results than ocean acidification.
- Many search engines allow the use of asterisks (*) to replace multiple characters. For instance, “marine eco*” could find results for “marine ecology,” “marine ecosystem,” etc.
Employing Boolean Operators
Boolean operators are powerful tools for refining your search:
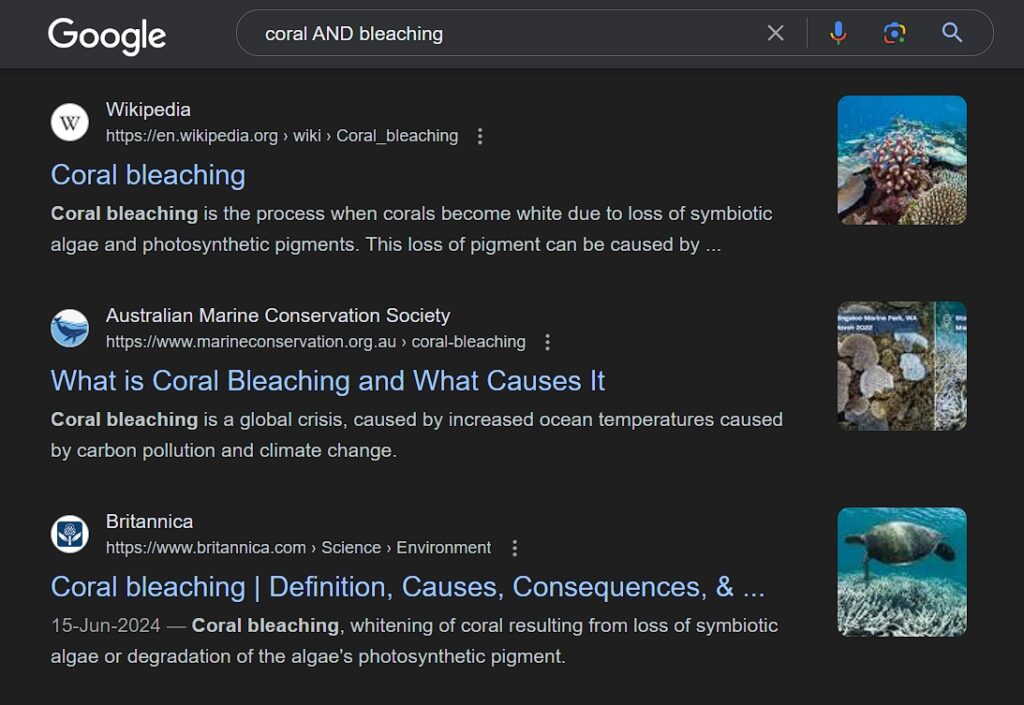
- AND: Use this to narrow your search. For example, “coral AND bleaching” will return results that include both terms.
- OR: This broadens your search. “coral OR reef” will find articles containing either term.
- NOT: This excludes specific terms. “coral NOT freshwater” will exclude results about freshwater corals.
- Parentheses: Use these to group terms together. “(coral OR reef) AND acidification” will search for articles about acidification in relation to either coral or reefs.
Example:
Let’s apply these tips to our earlier research question about ocean acidification and coral reefs. An effective search query might look like this:
(“ocean acidification” OR “seawater pH”) AND (“coral reef*” OR “Great Barrier Reef”) AND (impact* OR effect*) AND (2013..2024)
This query:
- Uses quotation marks for specific phrases
- Employs OR to include synonyms
- Uses AND to combine different aspects of the research question
- Includes a wildcard (*)
- Specifies a date range (adjust based on the search engine’s syntax)
Accessing Online Databases
While academic search engines provide a broad overview of available research, online databases often offer more specialized and comprehensive collections of scholarly articles.
Many of these databases are free to access, providing valuable resources for researchers at all levels.
Here is a list of Free Online Journals and Research Databases
- Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ) is a community-curated online directory that indexes and provides access to high-quality, open access, peer-reviewed journals. It covers various academic disciplines and is an excellent resource for finding freely available scholarly articles. Key features:
- Contains 20,566 journals from 134 countries
- Covers all areas of science, technology, medicine, social sciences, and humanities
- Allows searching at both journal and article level
- PubMed Central PubMed Central (PMC) is a free full-text archive of biomedical and life sciences journal literature. It’s maintained by the U.S. National Institutes of Health’s National Library of Medicine (NIH/NLM). Key features:
- Contains over 7 million full-text articles
- Focuses on biomedical and life sciences research
- Includes a mix of peer-reviewed articles and preprints
- ERIC (Education Resources Information Center) is an online library of education research and information sponsored by the Institute of Education Sciences (IES) of the U.S. Department of Education. Key features:
- Contains over 1.7 million records
- Provides access to educational literature and resources
- Includes journal articles, books, research syntheses, conference papers, and other education-related materials
- JSTOR is primarily a subscription service, it offers a selection of open-access content and free read-online access to a limited number of articles. Key features:
- Covers a wide range of academic disciplines, with particular strength in humanities and social sciences
- Provides access to some of the most established academic journals
- Offers a “Register & Read” program allowing free access to a limited number of articles
How to Use Database Filters and Advanced Search Options
To make the most of these databases, it’s crucial to understand and utilize their advanced search features and filters. While specific options may vary between databases, here are some common and useful features:
- Limit your search to articles published within a specific time frame for recent research or historical studies.
- Filter results by publication type, such as peer-reviewed articles, conference proceedings, or book chapters.
- Narrow your search to specific academic disciplines or sub-disciplines.
- Show only articles available in full text through the database.
- Restrict results to articles in specific languages.
- Search for works by particular authors or groups of authors.
- Use database citation tools to cite articles in various styles.
- Employ Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT) to refine your search.
- Use proximity operators to find terms within a certain word range of each other (e.g., “ocean acidification”~10).
- Apply truncation and wildcards (, ?) to search for word variations (e.g., “coral” for coral, corals, coralline).
Leveraging Institutional Resources
Institutional resources offer access to a wide range of high-quality research materials.
If you’re affiliated with a university or research institution, utilize these tools to enhance your research:
University Libraries and Databases
- Use the library catalog for physical and digital resources.
- Consult subject-specific guides for relevant databases and journals.
- Explore the Database A-Z List for specialized resources.
- Learn how to access resources remotely.
- Take advantage of librarian expertise through research consultations.
Interlibrary Loan Services (ILL)
- Check your library’s ILL policy.
- Provide accurate information when requesting items.
- Submit requests well in advance.
- Consider digital delivery for faster access.
- Respect loan periods to maintain good standing.
Institutional Repositories (IRs)
IRs are digital collections of an institution’s intellectual output, offering:
- Open access to many items
- Access to current and pre-publication research
- Opportunities for interdisciplinary discovery
- Networking possibilities with other researchers
- Access to grey literature
To maximize IR use:
- Learn the search interface and browsing options.
- Set up alerts for new additions in your field.
- Consider depositing your own work to increase visibility.
Exploring Specialized Research Networks
In addition to traditional academic databases and institutional resources, specialized research networks have emerged as valuable platforms for finding and sharing research articles. These networks not only provide access to a wide range of publications but also offer opportunities to connect with researchers in your field.
Some of the best research databases include:
ResearchGate

ResearchGate is a professional network for scientists and researchers. It combines elements of social media with a repository of research papers.
Key features:
- Over 20 million members from various scientific disciplines from over 190 countries
- Allows researchers to share papers, ask and answer questions, and find collaborators
- Provides metrics on article views, citations, and overall researcher impact
- Offers a Q&A section where researchers can seek expert opinions on specific topics
Academia.edu
Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers. It aims to accelerate the world’s research by promoting open access to scholarly articles.
Key features:
- Over 264 million registered users
- Allows users to upload papers, monitor their impact, and track the research of academics they follow
- Offers analytics on document views and profile visits
- Provides a jobs board for academic positions
SSRN (Social Science Research Network)
SSRN is a repository and international journal devoted to the rapid dissemination of scholarly research in the social sciences and humanities.
Key features:
- Focuses on early-stage research and working papers
- Covers a wide range of social sciences including economics, law, corporate governance, and more
- Allows researchers to share papers before peer review, enabling rapid dissemination of new ideas
- Provides download and citation statistics for papers
How to Network with Researchers and Access Publications?
These platforms offer unique opportunities to connect with fellow researchers and access cutting-edge research.
Here’s how to make the most of them:
- Create a comprehensive, up-to-date profile
- Share your research, including preprints and datasets
- Follow key researchers in your field
- Engage in discussions and Q&A sections
- Use search functions effectively; set up alerts
- Request access to papers when needed
- Analyze metrics to identify influential papers
- Join relevant groups or topics
- Respect copyright laws when sharing
- Use networking features for collaborations
Evaluating the Credibility of Sources
Distinguish credible, high-quality research from less reliable sources to ensure your research is built on a solid foundation.
Assessing Peer-Reviewed Journals:
- Consider the journal’s Impact Factor to gauge its influence in the field.
- Check if the journal is indexed in reputable databases like Web of Science, Scopus, or PubMed.
- Examine the composition of the journal’s editorial board for recognized experts.
- Look for regular publication schedules, as erratic ones may be a red flag.
- Verify that the journal clearly explains its peer review process.
- Check if the journal is associated with a respected professional organization or academic institution.
Checking the Author’s Credentials:
- Verify the author’s affiliation with recognized academic or research institutions.
- Review the author’s publication history in reputable journals.
- Ensure the author’s background aligns with the paper’s subject matter.
- Check how often the author’s work is cited by other researchers.
- Look up the author on professional networks like ResearchGate or Google Scholar.
- Check for disclosure of funding sources and potential conflicts of interest.
Identifying Predatory Journals:
- Consult resources like Beall’s List or the Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ).
- Be wary of poorly designed websites with grammatical errors.
- Be skeptical of journals promising unusually fast peer review and publication.
- Watch out for journals claiming an unusually wide range of topics.
- Avoid journals that send unsolicited emails asking for submissions.
- Be cautious of unclear fee structures or surprisingly low publication fees.
- Be wary of journals boasting non-standard impact metrics.
- Check for transparency regarding location, editorial board, and policies.
- Verify the journal’s policy for long-term preservation of articles.
- Be skeptical of unverified claims about indexing in major databases.
Consider multiple factors when evaluating source credibility. Read critically, assessing methodology, data analysis, and conclusions. Consult experienced researchers or librarians if unsure about a source.
Utilizing Reference Management Tools
Efficiently organize and cite sources using reference management tools to save time and reduce errors.
Here’re some popular reference management tools:
- EndNote: Commercial software integrating with Microsoft Word, offering desktop and online versions, numerous citation styles, and library sharing.
- Zotero: Free, open-source software with browser extension, device syncing, collaborative libraries, and word processor integration.
- Mendeley: Free manager and academic social network featuring PDF annotation, networking, automatic syncing, and paper recommendations.
Use Blainy for Easy Citation Creation:
Say goodbye to citation headaches! With Blainy AI, creating perfect citations is as easy as highlighting text.
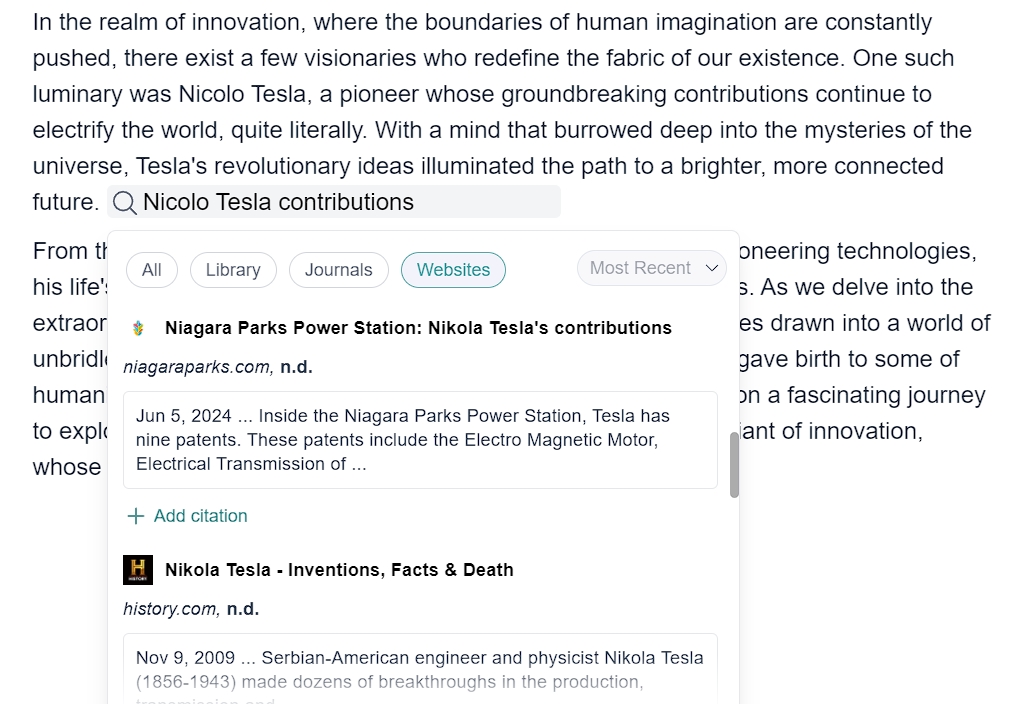
Here’s how our citation magic works:
- Simply select the text you want to cite and hit the “cite” button. It’s that simple!
- Blainy AI will conjure up a variety of references from journals, articles, and websites. Pick the one that fits your needs like a glove.
- APA? MLA? Harvard? Whatever citation style suits your fancy, Blainy’s got you covered.
Blainy AI efficiently generates a comprehensive bibliography at the end of your document, streamlining your research process and ensuring proper attribution.
Try Blainy Citation Feature Now
Remember, even superheroes need a sidekick. While Blainy AI does the heavy lifting, always give your citations a final once-over to ensure they’re picture-perfect. After all, with great citation power comes great responsibility!
Staying Updated with Alerts and Notifications
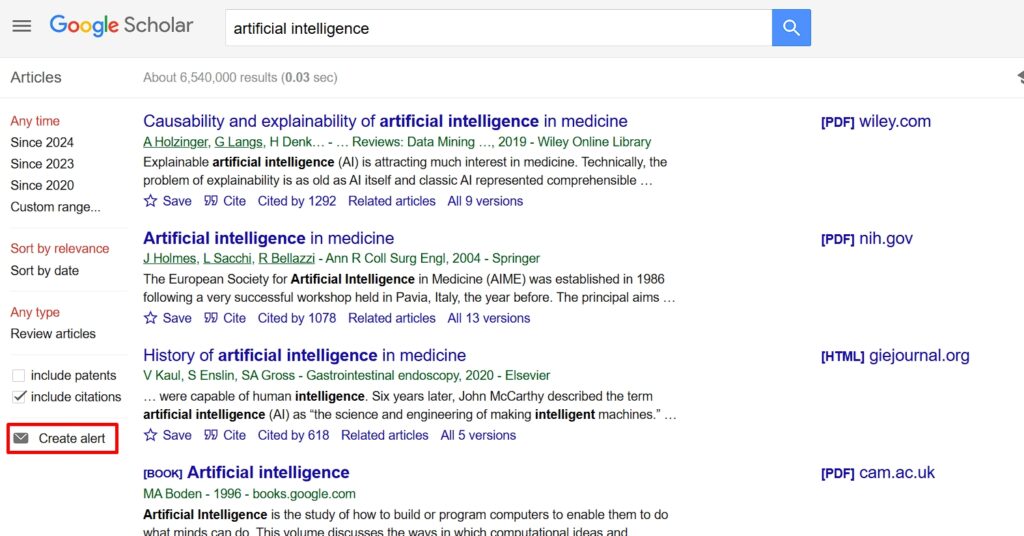
Here’s how to set up Google Scholar Alerts:
- Perform a search using relevant keywords.
- Click “Create alert” at the bottom of the search results page.
- Customize the alert: modify query, set frequency, and choose result relevance.
- Manage alerts via the menu icon > “Alerts”.
Subscribing to Journal Alerts:
- Identify key journals in your field.
- Visit journal websites and look for alert options.
- Choose preferences: table of contents, early view articles, specific topics.
- Manage subscriptions and set up email filters.
Additional Strategies you can use:
- Subscribe to major conference alerts for recent presentations.
- Set up alerts on preprint servers like arXiv or bioRxiv.
- Follow relevant hashtags and researchers on social media.
- Subscribe to professional society newsletters.
- Customize database alerts on PubMed, Web of Science, or Scopus.
Regularly review and adjust alert settings to maintain relevance and manageability, balancing information intake with productivity.
Conclusion
Finding research articles effectively is a vital skill for academic and professional success. By implementing the strategies outlined in this guide—from defining your research topic to staying updated with alerts—you’ll streamline your research process and access high-quality, relevant sources more efficiently.
Remember that finding research articles is an iterative process. Be prepared to refine your approach as you delve deeper into your topic. Stay open to new tools and platforms as the academic landscape evolves.
Ultimately, these skills are the foundation for meaningful contributions to your field. Whether you’re working on a class assignment or groundbreaking research, mastering the art of finding research articles will enhance the quality and impact of your work.
As you apply these techniques, you’ll develop a sharper eye for relevant literature and a deeper understanding of scholarly discourse in your field. With practice, you’ll navigate the world of academic research with confidence and expertise.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the best databases for finding research articles?
Popular databases for finding research articles include Google Scholar, PubMed, JSTOR, and Web of Science. Google Scholar offers a free, multidisciplinary search, while PubMed specializes in biomedical literature. JSTOR covers humanities and social sciences, and Web of Science provides comprehensive citation indexing across various fields. Consider also using subject-specific databases depending on your research area.
How can I access research articles for free?
Several options exist for accessing research articles without cost. Open-access journals, preprint servers, and institutional library resources are primary sources of free articles. You can also try academic social networks like ResearchGate or contact authors directly. Some public libraries offer database access, providing another avenue for free research material.
What’s the difference between primary and secondary research articles?
Primary research articles report original studies conducted by the authors, presenting new data or findings. They typically follow a standard format with introduction, methods, results, and discussion sections. Secondary research articles, on the other hand, analyze or summarize existing research, including literature reviews, meta-analyses, and systematic reviews. While primary articles form the foundation of research, secondary articles synthesize and interpret multiple primary sources.
How can I narrow down my search results when looking for research articles?
To refine your search results, employ strategies such as using Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT) and including specific keywords or phrases in quotation marks. Filter results by publication date, article type, or subject area, and utilize advanced search features in databases. Consider applying subject headings or MeSH terms in relevant databases, and refine results based on cited references or citing articles to find the most pertinent research for your needs.
How can Blainy AI help me with citations when working with research articles?
Blainy AI’s Citation Builder tool simplifies the citation process. Just highlight text and click “cite” to generate references in various styles (APA, MLA, Harvard, IEEE). It also creates a comprehensive bibliography, streamlining your research and ensuring proper attribution. While Blainy AI does the heavy lifting, always double-check your citations for accuracy.